前言
之前做的Java项目都是接手自别人,自己没有独立开发过。这几天抽空研究了一下Spring Boot做web开发,本文用作记录和参考使用。
准备工作
- 安装InteliJ IDEA;InteliJ IDEA基本上是Java和安卓开发必备工具,社区版可免费使用;
- 安装Mysql或Mariadb数据库。
使用Spring Boot + MyBatis + FreeMarker进行web开发
创建Spring Boot项目
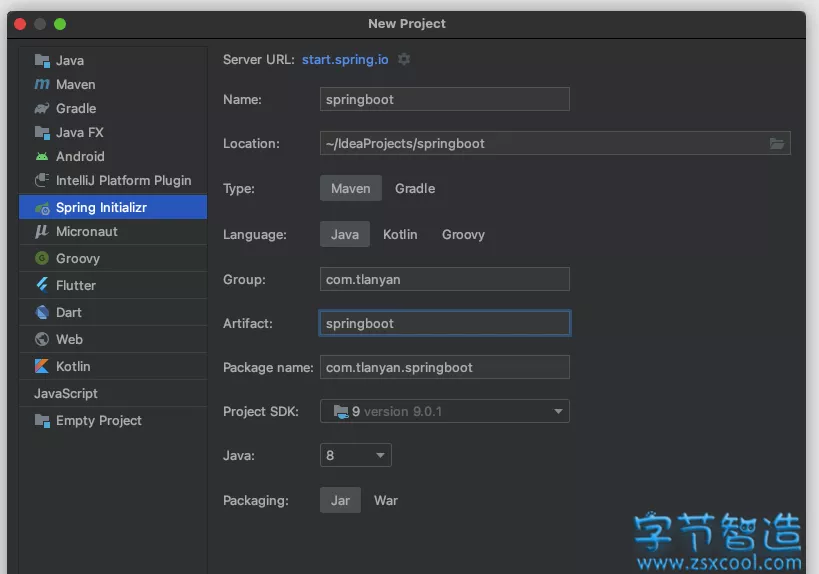
1. 打开IDEA,创建新项目,在引导对话框中选“Spring Initializr”,并自定义项目名称、包名,选择Java SDK和版本等:
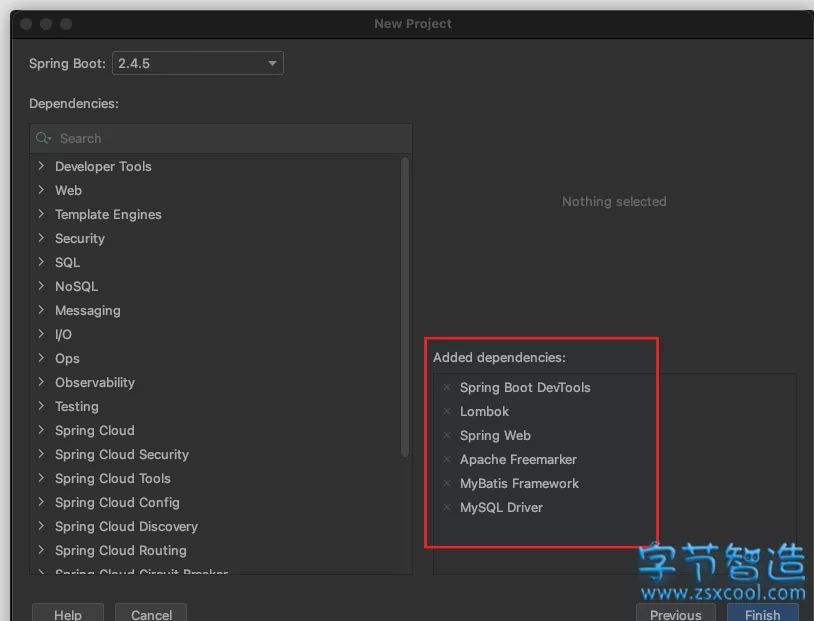
2. 选择Spring Boot DevTools、Lombok、Spring Web、Freemarker、MyBatis和MySQL这几个包:
生成的pom.xml内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.tlanyan</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. 因为没有配置数据库等,项目此时还无法启动。在根目录下创建 application.yml 文件,输入如下内容:
server:
port: 9000
spring:
freemarker:
template-loader-path: classpath:/templates
cache: true
suffix: .ftl
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/demo?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true
username: root
password: password
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:/templates/mapper/*Mapper.xml # mapper文件位置
type-aliases-package: com.tlanyan.springboot.entity如果熟悉properties文件的写法,可以直接编辑 src/resources文件夹下的application.properties文件
此时项目可以正常运行(Run -> Run “SpringbootApplication”)。
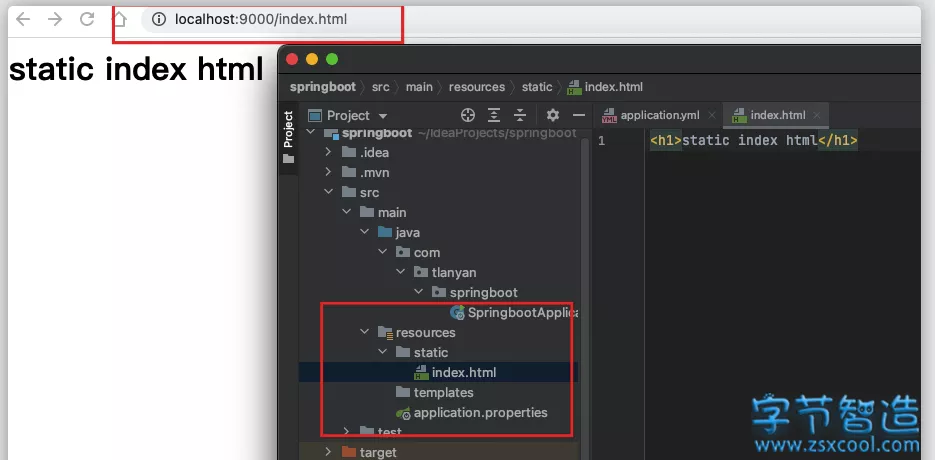
Spring Boot托管静态文件
静态资源放到 src/resources/static 目录下即可被访问到(添加新文件后需重新运行程序):
除了默认创建的static目录,静态资源文件还可以存放到public、resources和META-INF/resouces目录下。
Spring Boot + MyBatis + Spring MVC + FreeMarker
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
首先创建数据库表对应的实体类:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}然后创建Mapper接口:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.mapper;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
public User findById(Integer id);
public List getAll();
}以及在templates/mapper目录下创建UserMapper.xml文件(mapper文件需放到配置文件中的指定目录下,templates中的文件会被自动打包,因此我们选择这个位置):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tlanyan.springboot.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="findById" resultType="com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User">
SELECT * from user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="getAll" resultType="com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>接下来编写service层:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.service;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
public User findById(Integer id);
public List<User> getAll();
}以及其实现:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.service.impl;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User findById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.findById(id);
}
@Override
public List<User> getAll() {
return userMapper.getAll();
}
}然后controller层:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.controller;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/user/list")
public String List(Model model) {
List<User> users = userService.getAll();
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "user/index";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/{id}")
public String view(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model) {
User user = userService.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "user/view";
}
}最后编写Freemarker模板。在 resources/templates 文件夹下创建user文件夹,新建index.ftl输入下列内容:
<h1>User List</h1>
<ul>
<#list users as user>
<li>ID: ${user.id}, name: ${user.name}</li>
</#list>
</ul>以及 view.ftl:
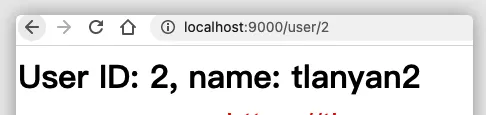
<h1>User ID: ${user.id}, name: ${user.name}</h1>
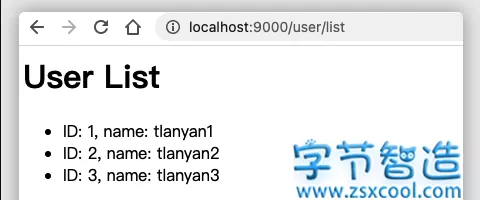
数据库创建user表,并灌入数据,运行程序,程序输出结果如下:
至此,Spring Boot + MyBatis + Spring MVC + Freemarker已经完全能正常工作。
Spring Boot使用Ehcache缓存
最后介绍使用Ehcache缓存增强程序性能。
首先引入Ehcache依赖。在pom.xml中引入ehcache:
...
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>然后在resouces目录下创建ehcache.xml配置文件(Spring Boot会扫描这个路径,因此请保证文件名正确),并输入以下内容:
<ehcache>
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
/>
<cache name="user"
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="true"
overflowToDisk="true"
diskPersistent="true"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="600"/>
</ehcache>其中:
- name:缓存名称。
- maxElementsInMemory:缓存最大个数。
- eternal:对象是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout将不起作用。
- timeToIdleSeconds:设置对象在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒)。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大。
- timeToLiveSeconds:设置对象在失效前允许存活时间(单位:秒)。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当eternal=false对象不是永久有效时使用,默认是0.,也就是对象存活时间无穷大。
- overflowToDisk:当内存中对象数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache将会对象写到磁盘中。
- diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区。
- maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘最大缓存个数。
- diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据。
- diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒。
- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)。
- clearOnFlush:内存数量最大时是否清除。
- diskStore 则表示临时缓存的硬盘目录。
然后在应用程序中配置开启缓存:
package com.tlanyan.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}以及在service层开启缓存:
package com.tlanyan.springboot.service.impl;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.entity.User;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.tlanyan.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
@Cacheable
public User findById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.findById(id);
}
@Override
@Cacheable
public List<User> getAll() {
return userMapper.getAll();
}
}注意,cacheNames的值需要在ehcache.xml中存在。
参考
- Spring Boot干货系列:(一)优雅的入门篇
- SpringBoot+MySQL+MyBatis的入门教程
- Springboot系列(四)web静态资源配置
- Spring Boot 缓存应用 Ehcache 入门教程
- Spring Boot2 系列教程(三十)Spring Boot 整合 Ehcache